Autres Cours
ESP32 RFID Door Lock System with Voice Alerts Using ESP-NOW Protocol
In this course, I will show you a wonderful project using the ESP-NOW communication protocol on ESP32 boards, combined with RFID to wirelessly trigger a voice alert.
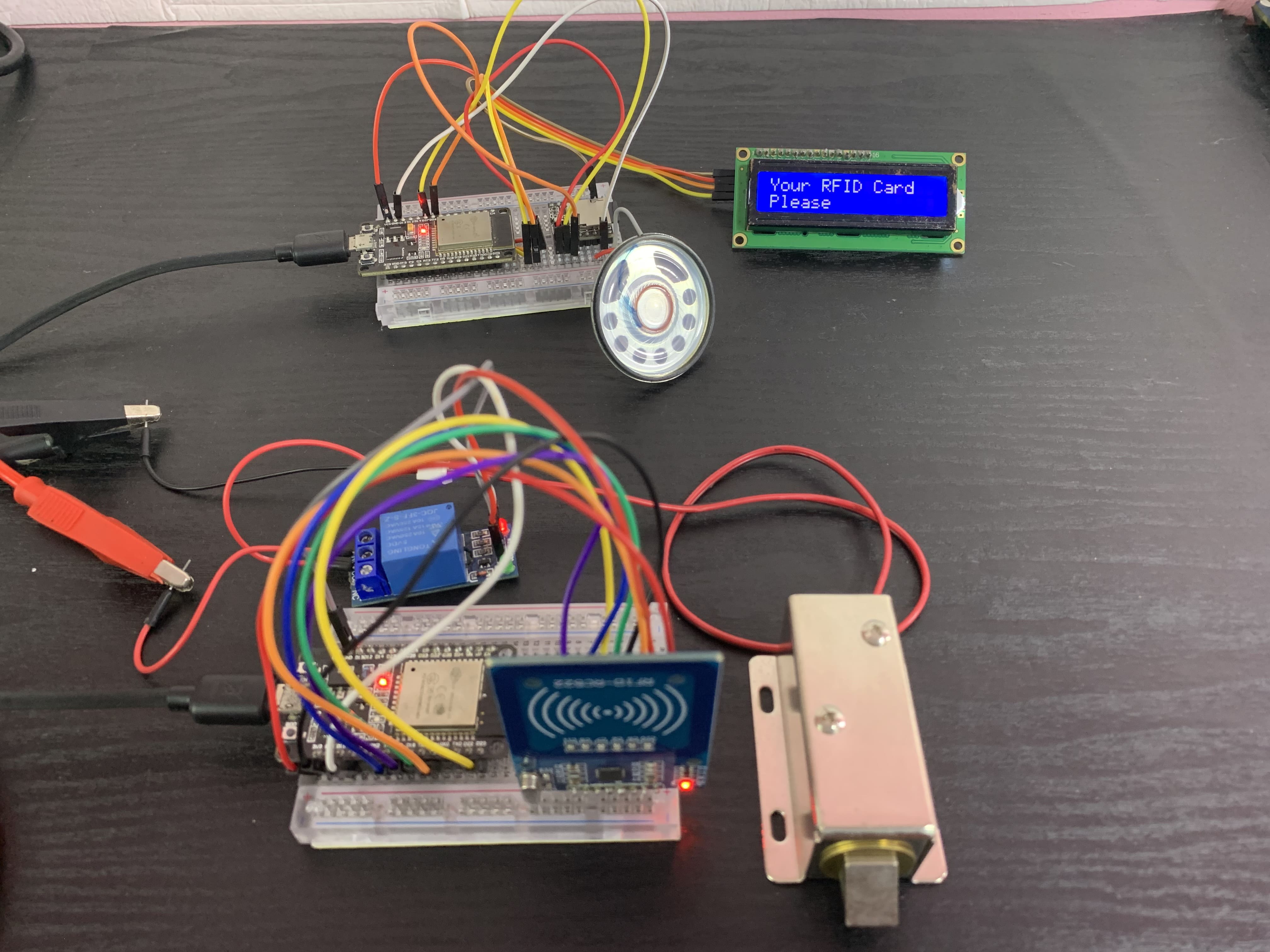
Description
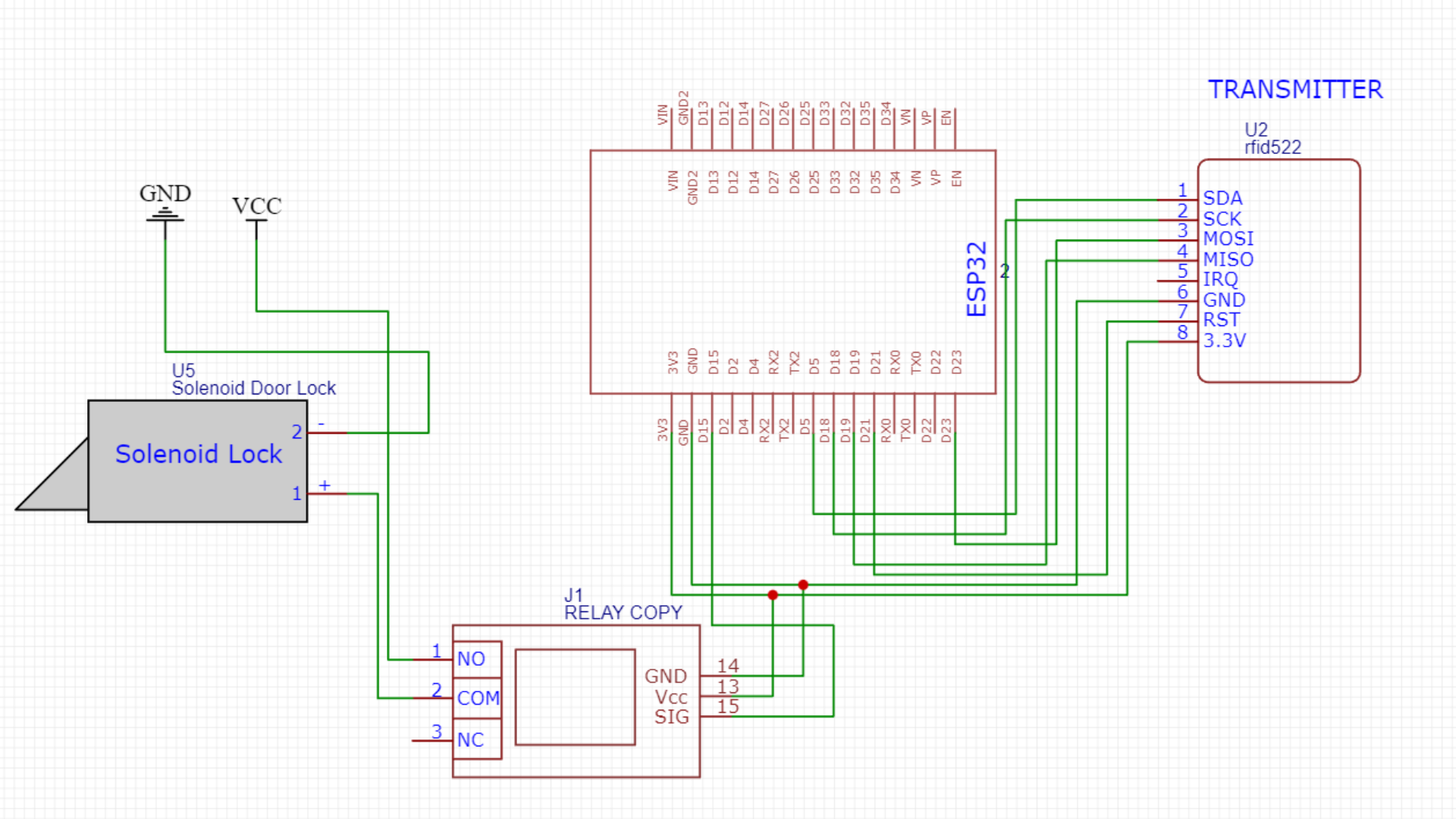
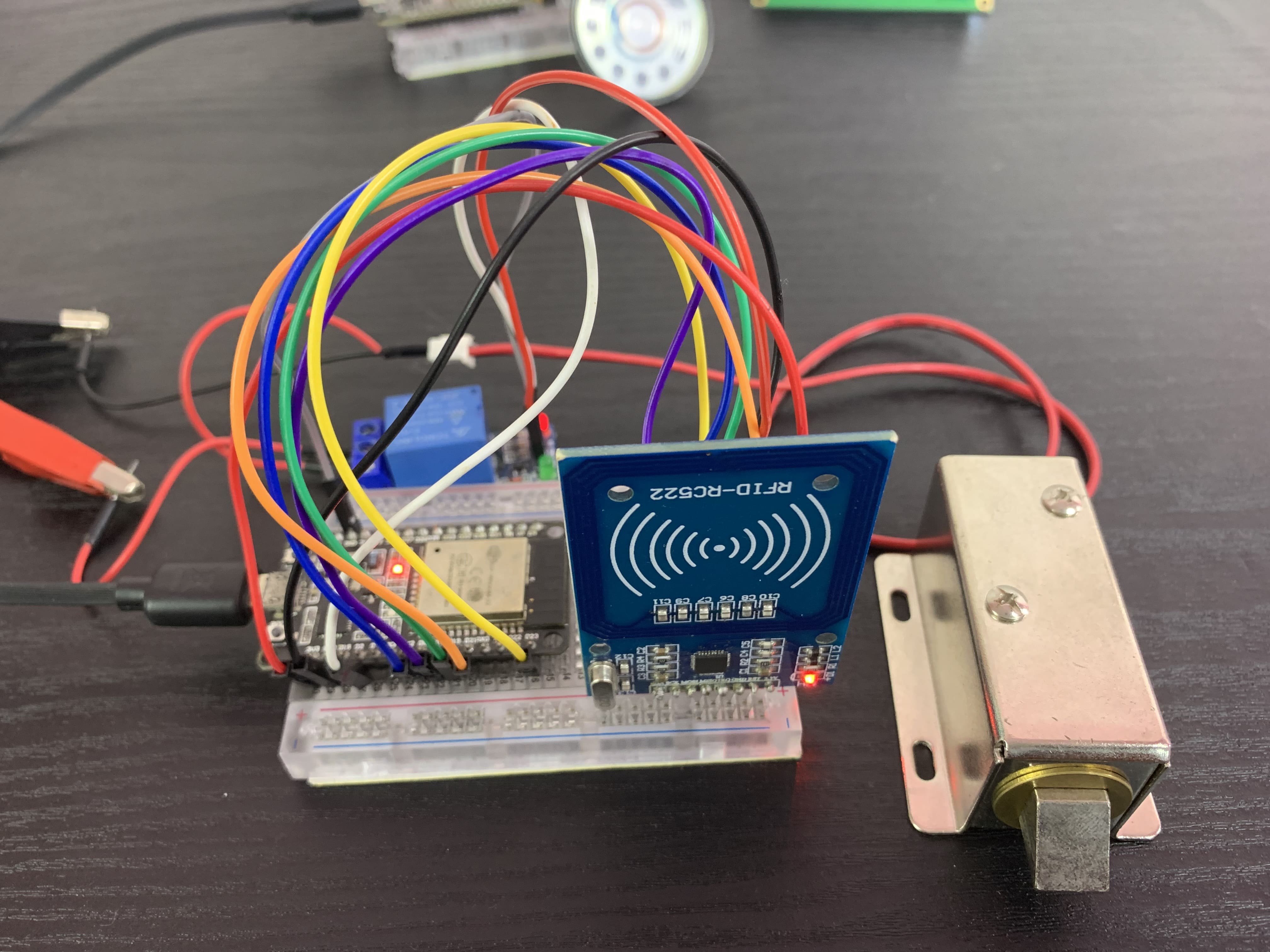
I used the ESP-NOW communication protocol to trigger voice alerts on the receiver board and display information on an LCD connected to it. On the transmitter board, I connected an RC522 RFID reader and a 12V solenoid door lock.
Components used
- Two ESP32 Bords
- Micro SD Card
- RC522 RFID Reader
- 12V Solenoid Door Lock
- 5V Relay Module
- 1W 20Ohm Speaker
- LCD Display
- An external Power Supply
- DFplayer Mini
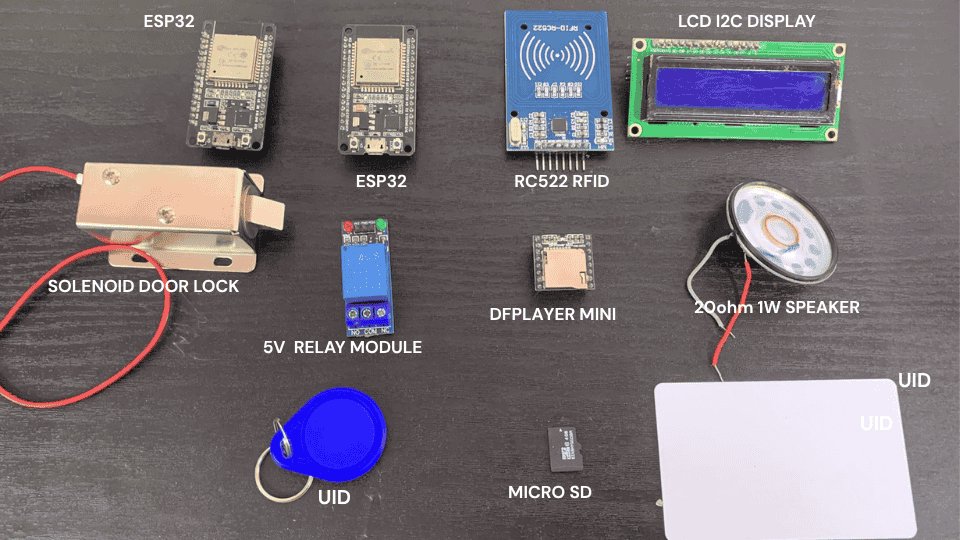
DFPlayer Mini Specifications
- Supply voltage: 3.2~5.0V
- Standby Current : 20mA
- Operating Temperature: -40~+70
- Protocol: Serial Communication
Supports FAT16, FAT32 file system, maximum support 32GB TF card 30 levels volume adjustable, 10 levels EQ adjustable.
The audio data is sorted by folder; supports up to 100 folders, each folder can be assigned to 1000 songs.
Note: If the MCU system is 5V. It is recommended connect a 1K resistor in series.
DFPlayerMini Pinout
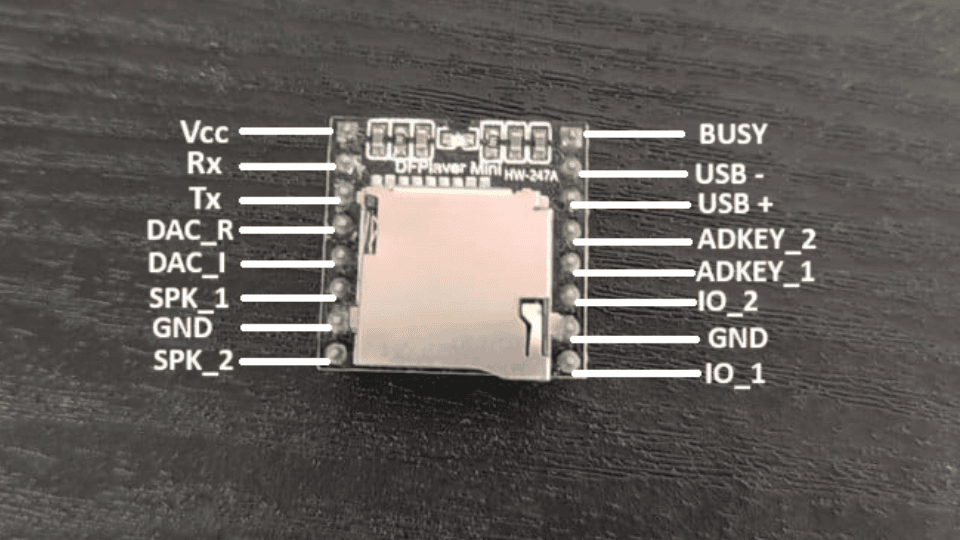
RC522 RFID Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 2.5V~3.3V
- Operating/Standby current: 13~26mA/10~13mA
- Communication Protocols: I2C and SPI and UART
- Operating Frequency: 13.56MHz.
RC522 RFID Pinout
Circuit Diagrams
Transmitter Circuit Diagram
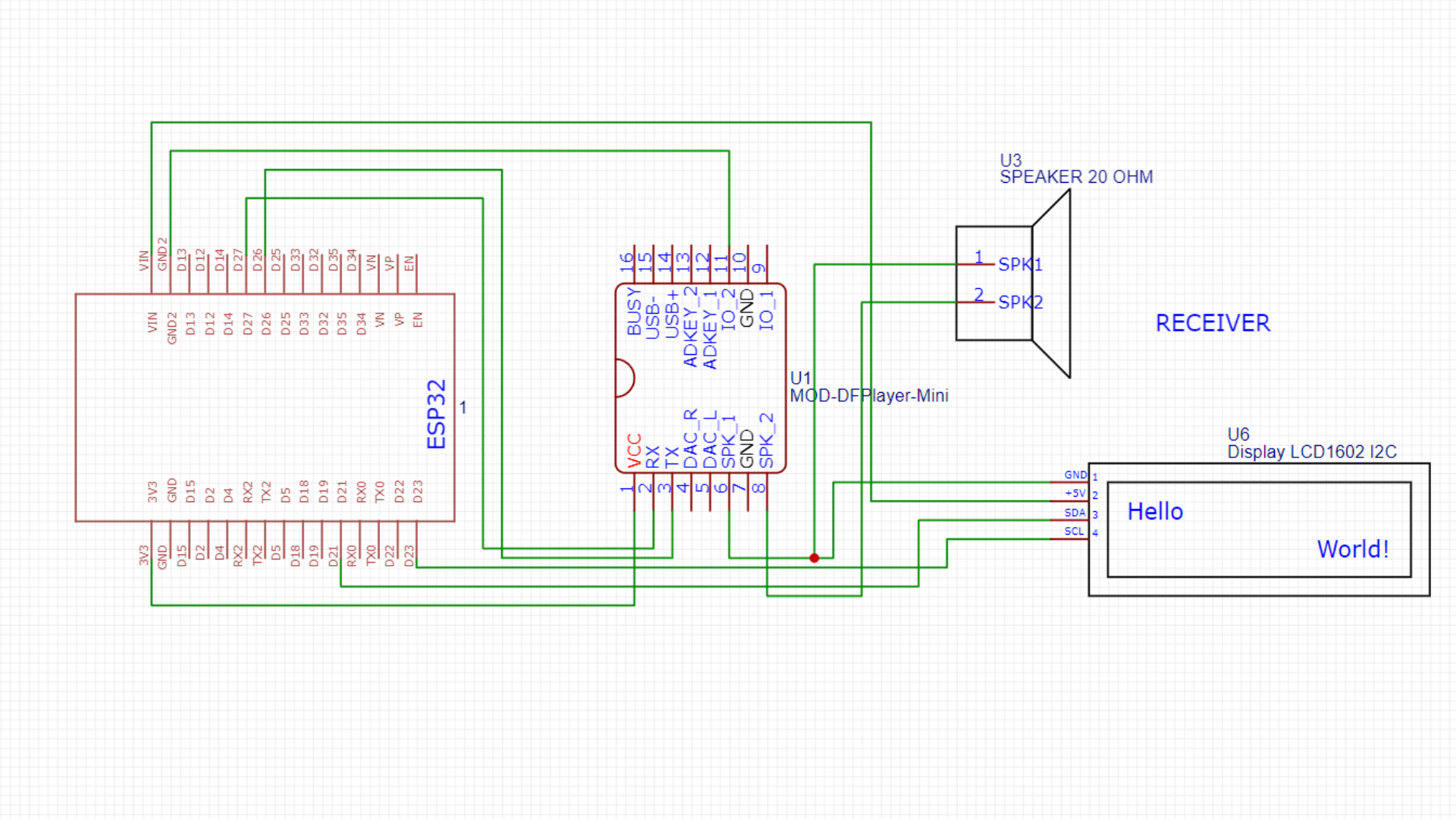
Receiver Circuit Diagram
Libraries to be installed
- DFRobotDFPlayerMini.h
- LiquidCrystal_I2C.h
Transmitter Code
// Include required libraries
#include <SPI.h> // Enables SPI communication for RFID reader
#include <MFRC522.h> // Library to interface with MFRC522 RFID reader
#include <Wire.h> // (Not used here, but included for I2C communication)
#include <esp_now.h> // Library to use ESP-NOW wireless communication
#include <WiFi.h> // Required to set Wi-Fi mode to station for ESP-NOW
// Define pin numbers for RFID and solenoid
#define SS_PIN 5 // Slave Select pin for RFID
#define RST_PIN 21 // Reset pin for RFID
#define SOLENOID_PIN 2 // Pin connected to solenoid lock
// Define the MAC address of the receiving ESP32
uint8_t broadcastAddress[] = {0x70, 0xB8, 0xF6, 0x5B, 0xED, 0xB0}; // Replace with your receiver ESP32 MAC address
// Define the data structure to send (no padding)
struct __attribute__((packed)) dataPacket {
bool state; // true if access granted, false otherwise
};
dataPacket packet; // Create an instance of dataPacket
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo; // Info about the peer to send data to
// Callback when ESP-NOW data is sent
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status) {
Serial.print("\r\nLast Packet Send Status:\t");
Serial.println(status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS ? "Delivery Success" : "Delivery Fail");
}
// Create RFID object
MFRC522 rfid(SS_PIN, RST_PIN); // Use defined pins for SPI communication
// Define the UID of the authorized RFID card
byte authorizedUID[] = {0x0B, 0x23, 0x9B, 0x15}; // Change this to match your card's UID
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Start serial communication for debugging
pinMode(SOLENOID_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set solenoid pin as output
digitalWrite(SOLENOID_PIN, HIGH); // Lock solenoid initially (HIGH = locked)
SPI.begin(); // Start SPI bus
rfid.PCD_Init(); // Initialize the RFID reader
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); // Set Wi-Fi mode to Station (required for ESP-NOW)
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) { // Initialize ESP-NOW
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent); // Register callback for data send status
// Register peer to send data
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, broadcastAddress, 6); // Copy MAC address
peerInfo.channel = 0; // Use default channel
peerInfo.encrypt = false; // No encryption
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK) { // Add peer
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
}
void loop() {
// Check if a new card is present
if (!rfid.PICC_IsNewCardPresent() || !rfid.PICC_ReadCardSerial()) {
return; // No card or failed to read card
}
Serial.print("UID tag: ");
String content = "";
// Print and build UID string
for (byte i = 0; i < rfid.uid.size; i++) {
Serial.print(rfid.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " ");
Serial.print(rfid.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
content.concat(String(rfid.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? " 0" : " "));
content.concat(String(rfid.uid.uidByte[i], HEX));
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
// Compare UID with authorized UID
bool authorized = true;
for (byte i = 0; i < rfid.uid.size; i++) {
if (rfid.uid.uidByte[i] != authorizedUID[i]) {
authorized = false;
break; // If any byte doesn't match, exit loop
}
}
packet.state = authorized ? 1 : 0; // Set packet state based on authorization result
esp_now_send(broadcastAddress, (uint8_t *) &packet, sizeof(packet)); // Send packet
Serial.println(packet.state); // Print access state (1 or 0)
delay(30); // Short delay to ensure packet is sent
if (authorized) {
Serial.println("Access Granted!");
digitalWrite(SOLENOID_PIN, LOW); // Unlock solenoid
delay(2000); // Keep it unlocked for 2 seconds
digitalWrite(SOLENOID_PIN, HIGH); // Lock again
} else {
Serial.println("Access Denied!");
}
rfid.PICC_HaltA(); // Stop communication with this card
}Transmitter Circuit
Receiver code
// Include necessary libraries
#include <esp_now.h> // ESP-NOW protocol for communication
#include <WiFi.h> // Required for WiFi functions (needed by ESP-NOW)
#include "Arduino.h" // Core Arduino functions
#include "DFRobotDFPlayerMini.h" // DFPlayer Mini library to control the MP3 module
#include <Wire.h> // I2C communication library
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> // Library for I2C-based LCD display
// Define software serial for non-ESP32 boards
#ifdef ESP32
#define FPSerial Serial1 // On ESP32, use hardware serial Serial1 for DFPlayer
#else
#include <SoftwareSerial.h> // For non-ESP32, include SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial FPSerial(26, 27); // RX = 26, TX = 27 (DFPlayer communication)
#endif
DFRobotDFPlayerMini myDFPlayer; // Create DFPlayer object
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2); // Initialize LCD with I2C address 0x27, 16 columns and 2 rows
// Structure for received ESP-NOW data
struct __attribute__((packed)) dataPacket {
bool state; // Boolean representing access status (authorized or not)
};
unsigned long previousMillis = 0; // Store last time LCD was updated
const long interval = 1000; // Interval time to keep welcome message (1 second)
bool playStarted = false; // Flag to indicate playback start
bool dataReceived = false; // Flag to indicate new data received
// Object to store incoming data
dataPacket receivedPacket;
// Callback function called when ESP-NOW receives data
void OnDataRecv(const esp_now_recv_info* info, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len) {
memcpy(&receivedPacket, incomingData, sizeof(receivedPacket)); // Copy received data into our structure
Serial.print("UID State: ");
Serial.println(receivedPacket.state); // Print UID state to Serial
dataReceived = true; // Set flag to true
}
void setup() {
#ifdef ESP32
FPSerial.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, 26, 27); // ESP32-specific Serial1 initialization (RX, TX)
#else
FPSerial.begin(9600); // For other boards, just begin serial
#endif
Serial.begin(115200); // Start Serial for debug output
lcd.init(); // Initialize LCD
lcd.backlight(); // Turn on LCD backlight
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Initializing..."); // Print init message
delay(2000);
Serial.println(F("DFRobot DFPlayer Mini Demo"));
Serial.println(F("Initializing DFPlayer..."));
// Initialize DFPlayer and check for errors
if (!myDFPlayer.begin(FPSerial)) {
Serial.println(F("Unable to begin:"));
Serial.println(F("1. Recheck connection!"));
Serial.println(F("2. Insert SD card!"));
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("DFPlayer Error!");
while (true); // Stop program here if DFPlayer fails
}
Serial.println(F("DFPlayer Mini online."));
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("DFPlayer Ready"); // Show ready message
delay(1000);
myDFPlayer.volume(30); // Set maximum volume (0-30)
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); // Set ESP32 as WiFi station (required for ESP-NOW)
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("ESP-NOW Init Failed");
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("ESP-NOW Error!");
return; // Stop further execution if ESP-NOW fails
}
esp_now_register_recv_cb(OnDataRecv); // Register callback to handle received data
myDFPlayer.play(1); // Play welcome/default track
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
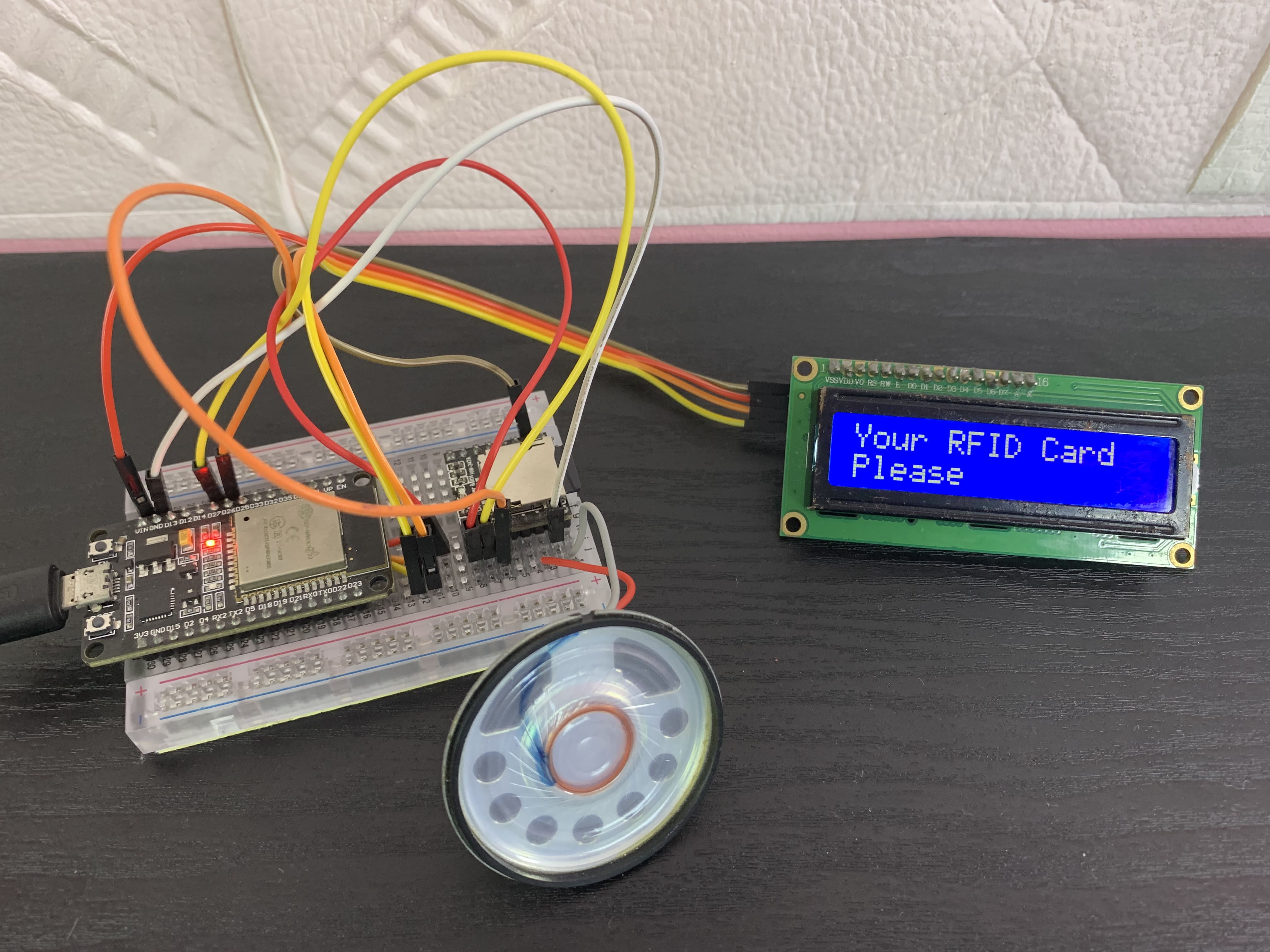
lcd.print("Your RFID Card"); // Show default message
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Please");
}
void loop() {
// If data was received, process it
if (dataReceived) {
dataReceived = false; // Reset flag
playStarted = true; // Set playback flag
previousMillis = millis(); // Save current time
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
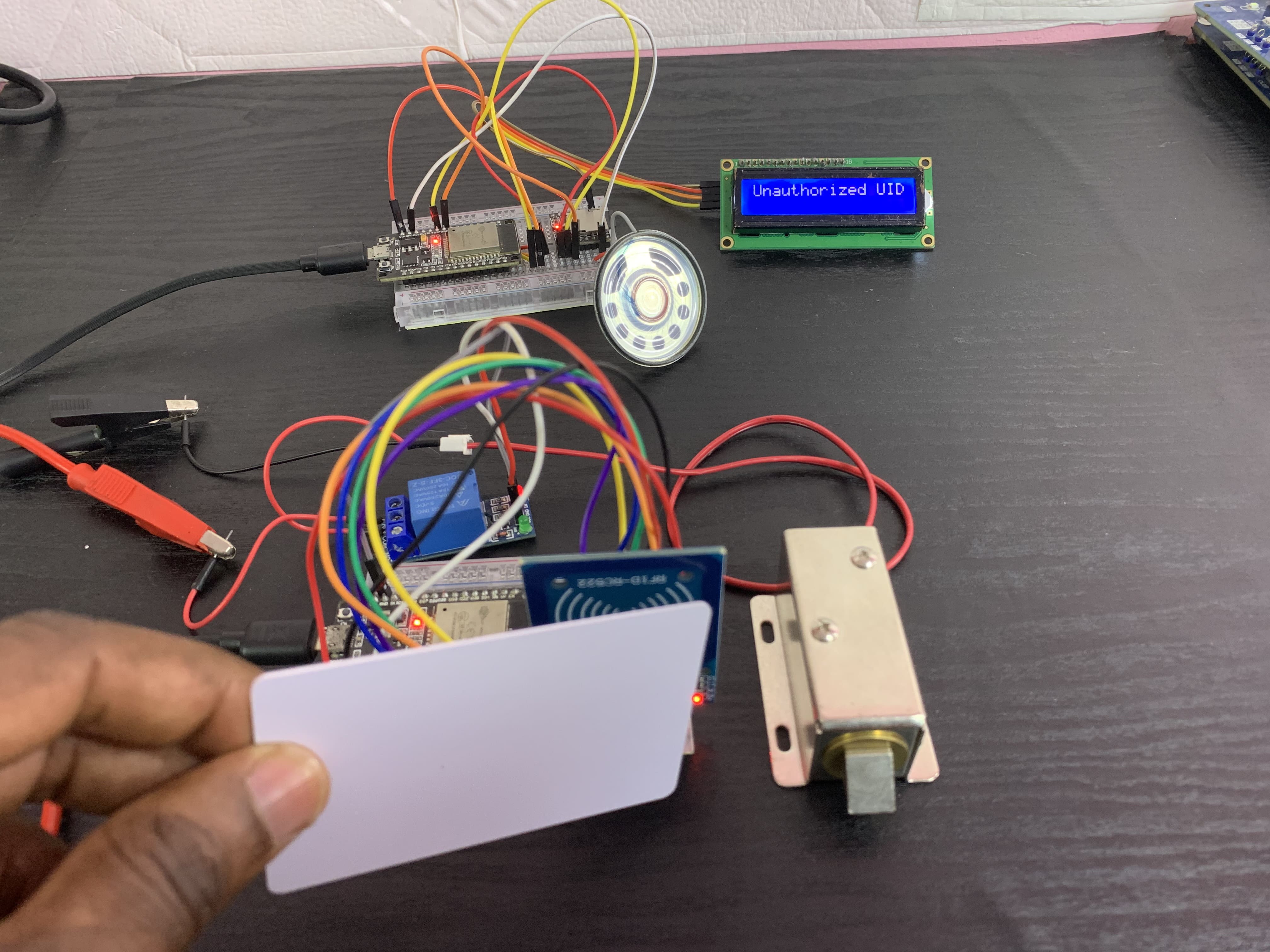
if (receivedPacket.state == 0) {
myDFPlayer.play(1); // Play unauthorized UID audio
lcd.print("Unauthorized UID"); // Show message
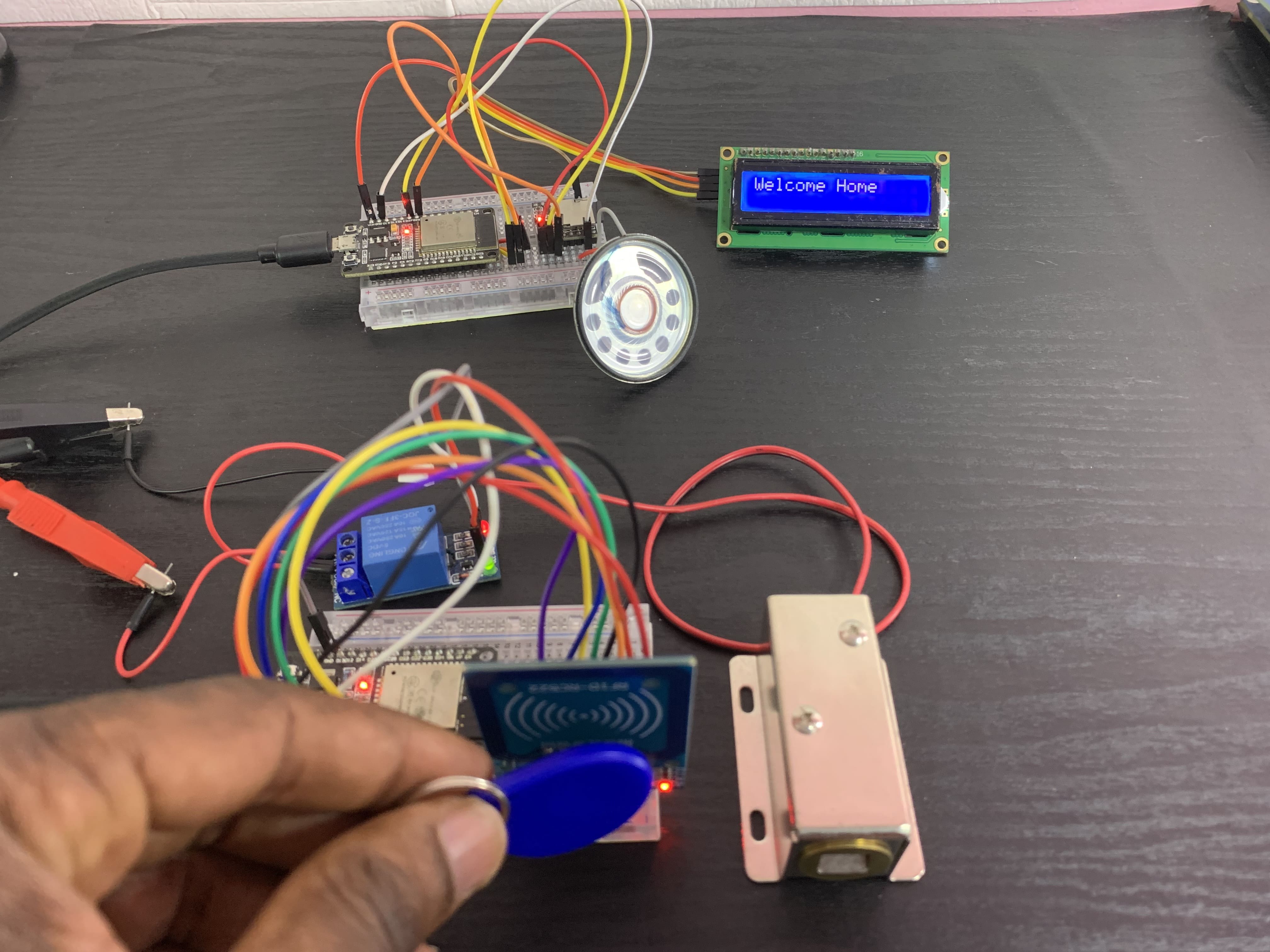
} else {
myDFPlayer.play(2); // Play welcome audio
lcd.print("Welcome Home"); // Show message
}
}
// After a delay, restore the LCD to default message
if (playStarted && (millis() - previousMillis >= interval)) {
playStarted = false; // Reset flag
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Your RFID Card"); // Restore default message
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Please");
}
}Audios used
Receiver Circuit
Explanation
When the RFID reader detects an unauthorized UID, the transmitter board will wirelessly trigger a voice alert—'Unauthorized UID Detected'—on the receiver board, and the 12V solenoid door lock will remain locked. However, when the RFID reader detects a valid UID, the transmitter board (ESP32) will send a signal to trigger another voice alert—'Welcome Home'—on the receiver board, and the 12V solenoid door lock will unlock for 2 seconds.
Wrong UID Detection
Correct UID Detection
Application
- Smart Home Access Control
- Office Entry Management
- School/University Lab or Classroom Access
- Office Entry Management
- School/University Lab or Classroom Access
- Warehouse or Storage Room Security
- Hotel Room Door Automation
- Church or Community Centers
- Garage or Gate Entry System
- Industrial Machine Access Control
- Medical Facility or Pharmacy Access
Produits Recommandés
No products are available
